Knowledge: Red Hat Satellite 6 things to remember
Architecture
Key components built on mature open source projects:
- Puppet: Configuration Management
- FOREMAN: Provisioning
- Pulp: Repository Management
- KATELLO: Content/LifeCycle Management
- Candlepin: Subscription Management
Terminologies
Orginization: Organizations divide hosts into logical groups based on ownership, purpose, content, security level, and other divisions. Subscription manifests can be imported only into a single organization. Satellite will not upload a certificate that has already been uploaded into a different organization.
Manifests: Manifest files are signed ZIP files, which provide SKU-level mapping of products, including SLA and expiration dates. Manifests contain information in JSON format and are fairly cryptic. Red Hat Enterprise Linux include the rct tool, which you use to work with manifests.
LifeCycle Management: The lifecycle envirnment is a means to manage versions with in the datacenter. By default all content that come in to Satellite goes into the evnirnment called ‘Library’ from the Library administrators can move content to other envirnments such as Dev, Testing, Prod etc
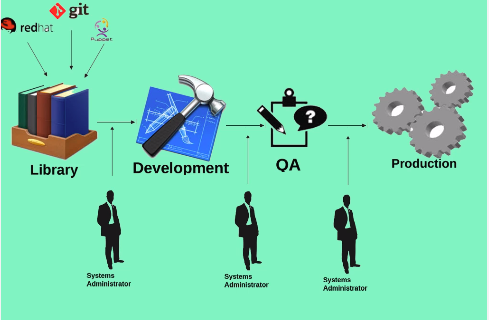
The application life cycle is divided into life cycle environments that mimic each stage of the life cycle. Life cycle environments are linked in an environment path. You can promote content along the environment path to the next life cycle stage when required.
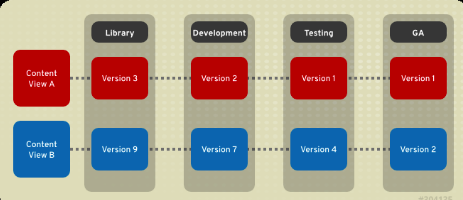
Content Views: A repository (yum/Puppet) provides storage for a collection of content. You can associate a repository with specific content views. Content views are managed selections of content that contain one or more repositories with optional filtering. Published content views are used with life cycle environments. Content View is a new feature that comes with satellite 6, it is means for modeling content
Composite content view: Is a combination of multiple content views. We can take this composite content view and promote it into over lifecycle environment
Discovery: RH Satellite can automatically identify non provisioned host
Hammer: Is the cli tool to manage Red Hat Satellite 6
Activation Key: Activation keys are preset keys used when registering the host. They defines life-cycle environment, host collection, organization, subscription usage limit.
Host Groups: Defines a set of default values for a host
Disconnected Satellite
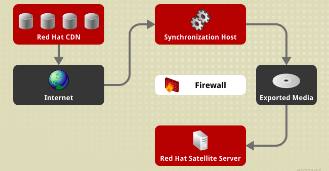
Red Hat Satellite Server can still provision systems with the latest security updates, errata, and packages. This is achieved by using katello-disconnected utility and Synchronization host
synchronization host is an intermediary system with an Internet connection. This host is in a separate network from the Satellite server.
The synchronization host download content through Pulp. The content is then exported onto physical media and transferred to the disconnected Satellite server.
FOREMAN Plugins
foreman-tasks: Provides Dynflow infrastructure for using Dynflow for managing the tasks.
foreman_bootdisk: Satellite plug-in for creating iPXE-based boot disks to provision hosts without the need for PXE infrastructure.
foreman_discovery: MaaS Discovery plug-in engine for Satellite.
foreman_docker: Provisions and manages Docker containers and images from Satellite.
foreman_openscap: Satellite plug-in for managing security compliance reports.
foreman_remote_execution: Brings remote execution to Satellite, completing the configuration management functionality with remote management functionality.
foreman_theme_satellite: Enables building themes for Satellite.
Katello: Content and subscription management plug-in for Satellite.
redhat_access: Adds Red Hat Access knowledgebase search, case management, and diagnostics to Satellite.
System Requirements
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Server 64-bit
- A minimum of 2 CPU cores, 4 CPU cores are recommended
- A minimum of 12 GB memory is required for the Satellite Server to function, 16 GB of memory or more is recommended
- A unique host name, which can contain lower-case letters, numbers, dots (.) and hyphens (-)
- A current Red Hat Satellite subscription
- Full forward and reverse DNS resolution using a fully-qualified domain name
The XFS file system is recommended for Red Hat Satellite 6 because it does not have the inode limitations that ext4 does.
Repository Required :
Red Hat Enterprise Linux $releasever - $basearch
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Software collections
Satellite6.x
Installing Satellite 6
Instead of having distinct installation programs for Satellite and Capsule (katello-installer, capsule-installer), Satellite 6.3 has “scenarios” to determine which features are installed, Satellite-installer –list-scenarios
yum install satellite -y
#list satellite scenarios
satellite-installer --list-scenarios
#The installer can be run multiple times to add, disable, and configure features.
satellite-installer --foreman-initial-organization hazaq-me \
--foreman-initial-location dxb \
--scenario satellite \
--foreman-proxy-tftp true \
--foreman-proxy-dhcp true \
--foreman-proxy-dhcp-gateway "192.168.0.2" \
--foreman-proxy-dhcp-interface "eth0" \
--foreman-proxy-dhcp-range "192.168.0.200 192.168.0.250" \
--foreman-proxy-dns true \
--foreman-proxy-dns-forwarders "192.168.0.10" \
--foreman-proxy-dns-interface "eth0" \
--foreman-proxy-dns-reverse 0.168.192.in-addr.arpa \
--foreman-proxy-dns-server "127.0.0.1" \
--foreman-proxy-dns-zone "hazaq.me" \
--foreman-admin-password 'password'
#Alternatively, this can be done interactively with satellite-installer -i.
After installing you can set the default Orginization and Location by going in to
Admin User → My Account
Set Up Hammer:
mkdir ~/.hammer
touch ~/.hammer/cli_config.yml
chmod 600 ~/.hammer/cli_config.yml
cat > ~/.hammer/cli_config.yml << EOF
:foreman:
:host: 'https://satellite.hazaq.me/'
:username: 'admin'
:password: 'password'
EOF
hammer organization list
Next step is to download the manifest for rh customer portal. And import it into satellite 6 by Select Content → Red Hat Subscriptions
Now we can select repos that we need by going into Content → Red Hat Repositories
Red Hat Satellite Tools 6.2 Repo should be selected.
Once the repos are select we can start synchronize content. To do that we need to select Content → Sync Status then check the produects and click Synchronize Now
you can see the sync progress by useing the below log file
tail -f /var/log/foreman/production.log
Register Client:
The date and time should be correct and synchronized on client and satellite server.
Virtualized environments should have ntpd or chronyd.
Red Hat Subscription Manager should be installed and updated.
YUM and yum-rhn-plugin should be updated.
#Download and the CA intallation rpm
wget http://satellite.hazaq.me/pub/katello-ca-consumer-latest.noarch.rpm
yum -y install katello-ca-consumer-latest.noarch.rpm
#To verfy that CA is installed run
grep -i baseurl /etc/rhsm/rhsm.conf
#Now we can register this system to the satellite server
subscription-manager register --org=hazaq-me --environment=Library
subscription-manager attach --pool <ID>
#Enable Satellite tools which has the katello agent
subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-7-server-satellite-tools-6.2-rpms
#Install katello agent
yum -y install katello-agent
Puppet
You can leverage puppet with satellite, run below command on client to install and enable puppet
yum -y install puppet
systemctl enable puppet
/usr/bin/puppet config set server satellite.hazaq.me --section agent
/usr/bin/puppet config set ca_server satellite.hazaq.me --section agent
The first time you run Puppet on a client system and connect it to the master, the agent creates an SSL certificate for itself and sends it to the master. The master signs the certificate and returns it to the agent.
puppet agent --test --onetime
Output should look something like this.
Info: Creating a new SSL key for localhost.integra.lan
Info: Caching certificate for ca
Info: csr_attributes file loading from /etc/puppet/csr_attributes.yaml
Info: Creating a new SSL certificate request for localhost.integra.lan
Info: Certificate Request fingerprint (SHA256): BB:72:25:D0:7D:99:74:AF:17:B2:2E:9E:C4:19:2B:5A:96:44:A9:47:5C:8B:4D:13:13:B7:A3:1E:CA:DD:77:13
Info: Caching certificate for ca
Exiting; no certificate found and waitforcert is disabled
In the Satellite 6 web interface, select Infrastructure → Capsules.
In the row with the Satellite server’s host name, at the right in the Actions column, click the down arrow and select Certificates.
To the right of your listed client system, click Sign.