Containers and Docker
Docker
Docker is a computer program that performs operating-system-level virtualization also known as containerization.Docker uses a client-server architecture.
Client
Docker has command-line tool responsible for communicating with a server using a RESTful API to request operations.
Server
This service, which runs as a daemon on an operating system, does the heavy lifting of building, running, and downloading container images.
Images
Images are read-only templates that contain a runtime environment that includes application libraries and applications.
Registries
Registrie stores those images for an easy deploy, just like git Registries could be private or public.
Containers
Containers are segregated user-space environments for running applications isolated from other applications sharing the same host OS.
Docker uses following Linux kernel functionality.
Namespaces
In a namespace, only processes that are members of that namespace can see those resources. The kernel can place specific system resources that are normally visible to all processes into a namespace.
Control groups or cgroup
cgroups is a Linux kernel feature that limits, accounts for, and isolates the resource usage of a collection of processes.
Creating Docker Container Images
There are two approaches.
Using a Dockerfile: Container images can be built from a base image using a set of steps called instructions. Each instruction creates a new layer on the image that is used to build the final container image.
Using a running container: An immutable image is used to start a new container instance and any changes or updates needed by this container are made to a read/write extra layer. This is not a recommended approach because the image size might become large due to unnecessary files.
Installing Docker
Installing docker ce (community edition) is simple just run the below command.
wget -qO https://get.docker.com/ | sh
systemctl start docker.service
#Verify docker is installed, below command should show you both client and server versions.
docker version
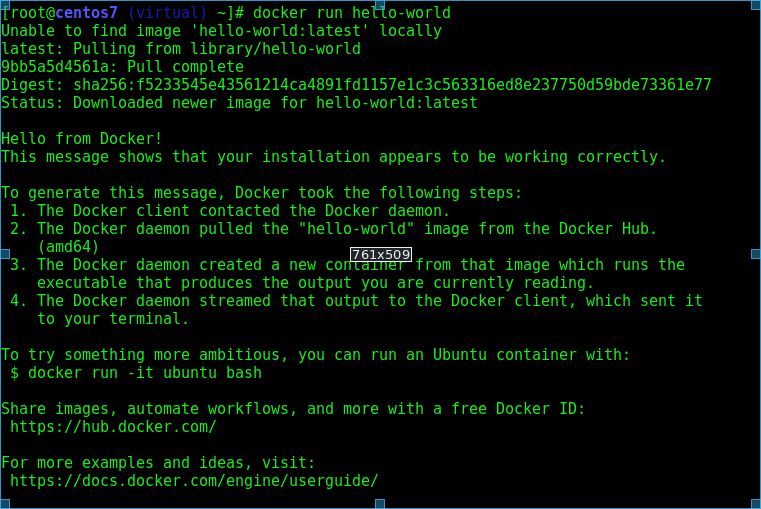
Lets start playing with docker.
docker run hello-world
what happened ?
# look for all containers
docker ps -a
# show images
docker images
Container Networking
Three Importent things to understand container networking.
Container Network Model (CNM): CNM is the design behined the container networking.
Libnetwork: Libnetwork is the implementation of CNM
Drivers: The type of Driver define what kind of network will be created inside a container it could be Bridge, VLAN etc. There could be 3rd party Drivers as well also know as Remote Drivers.
In short Libnetwork provides the foundation while Drivers sits on top and CNM is just the design model used to implement Libnetwork and Drivers.
CNM
CNM has three main constructs that needs to be understood.
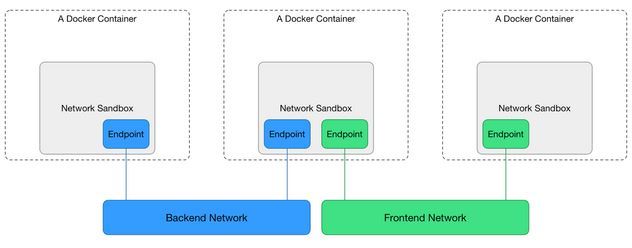
Sandbox: It is a namespace an Isolated area to create network stack.
Endpoint: Endpoint are the interfaces inside the container.
Network: Endpoint are created out of a network and those endpoints can talk with each other.
#List all the networks
docker network ls
docker network inspect bridge
Kubernetes
Kubernetes is an open-source container-orchestration system for automating deployment, scaling and management of containerized applications. Kubernetes have a master node architecture.
Master
In general we keep the master free of user workloads. Kubernetes master has 4 main components.
Apiserver: Is the front end for users to manager Kubernetes. Available through RESTful APIs.
KV Store: Uses etcd as the key value store, this is were the state of cluster is stored.
Controller: Controller monitors the etcd database for changes and applies to mantain desired state.
Scheduler: Scheduler ensures that pods are only placed on nodes that have sufficient free resources, it ties to spread pods from the same set across nodes, it tries to balance out the resource utilization of nodes, etc.
Node
Kubelet: Register a node with the cluster, it carry out the task assigned by the master and reports back. It also exposes an endpoint on the port 10255 where we can inspect the node.
Engine: Container engine could be either docker or rkt by default its docker, engine is responsible for managing the containers.
Proxy: Take cares of networking inside a node like assigning IPs creating load balance services etc.
replication controller vs deployment
Deployments are a newer and higher level concept than Replication Controllers. They manage the deployment of Replica Sets (also a newer concept, but pretty much equivalent to Replication Controllers), and allow for easy updating of a Replica Set as well as the ability to roll back to a previous deployment.
Config Map
Config Map is key value store (like Python dict object) and lives in etcd.
It lets you modify application behaviour without recreading a pod. Config Map are liked to there respective pods.
$ kubectl create configmap myconfig --from-literal=debug=false